Overtime isn’t automatically good or bad—it’s a tool. Used intentionally, it boosts productivity and profits. Mismanaged, it drains budgets and burns out employees. This guide breaks down the real cost of overtime, when to use it, when to avoid it, and how UKG + hrPad give you real-time control.
Table of Contents
Uncontrolled overtime inflates payroll by 22%. Strategic overtime boosts profits by 8%.
The Overtime Paradox: Your Most Expensive Tool Can Be Your Biggest Asset
Here’s the uncomfortable truth about overtime that most workforce managers won’t admit: they have no idea whether their overtime spend is helping or hurting their bottom line.
Consider two companies, each spending $250,000 annually on overtime:
Company A uses overtime strategically—covering unexpected demand spikes, retaining top performers with extra earning opportunities, and avoiding the cost of hiring additional full-time employees with benefits. Their overtime investment generates an estimated $270,000 in value. Net gain: $20,000.
Company B has runaway overtime—chronic understaffing, poor scheduling, inefficient processes, and managers who’ve lost control of their labor budgets. Their $250,000 overtime spend creates only $195,000 in value while burning out their workforce. Net loss: $55,000.
Same overtime spend. $75,000 difference in outcome.
The difference? One company manages overtime intentionally. The other lets overtime manage them.
This playbook will help you become Company A.
The True Cost of Overtime (It’s Not Just 1.5x)
Most managers think overtime costs 50% more than regular time. If you’re paying someone $20/hour, overtime is $30/hour. Simple math, right?
Wrong.
Here’s what overtime actually costs when you account for the hidden expenses:
Direct Costs:
- Base premium: 1.5x regular pay
- Double-time scenarios: 2x in some states (CA after 12 hours/day)
- Increased FICA taxes (employer portion)
- Higher workers’ comp premiums (based on total payroll)
Indirect Costs:
- Productivity decline: Studies show 20-30% reduced efficiency after 8 hours
- Error rates: Increase by 50% in hour 10-12 of a shift
- Safety incidents: 60% more likely during overtime hours
- Turnover acceleration: Mandatory overtime is the #2 reason frontline workers quit
- Manager time: 3-4 hours/week managing overtime schedules and approvals
Opportunity Costs:
- Delayed hiring decisions: “We’ll just run OT for another month”
- Process improvements ignored: Overtime masks inefficiency
- Training postponed: Too busy covering shifts to develop people
When you factor in everything, that $30/hour overtime can cost you $42-48/hour in real economic impact.
A single employee working 10 hours of overtime weekly costs you an extra $18,720 annually—or enough to hire a part-time employee at $12/hour for 30 hours/week.
When Overtime Helps Your Business
Despite the costs, strategic overtime is often your best option. Here’s when to embrace it:
1. Short-Term Demand Spikes
Holiday rushes, seasonal peaks, unexpected orders—when you know the demand is temporary (2-6 weeks), overtime beats hiring someone you’ll have to lay off.
Example: A retailer facing Black Friday traffic would lose millions by being understaffed. Scheduled overtime with adequate rest periods between shifts maintains service without permanent increases in headcount.
2. Specialized Skills Coverage
When only 2-3 employees can perform a critical task, overtime might be cheaper than the months needed to train replacements.
Example: A manufacturing plant with specialized equipment operators pays overtime rather than risk production errors from undertrained staff.
3. Employee Retention & Satisfaction
Many hourly workers want overtime opportunities. Denying them can drive them to competitors.
Example: A warehouse worker earning $17/hour values the ability to earn $25.50/hour during peak periods. Cutting all overtime could trigger turnover.
4. Avoiding Benefits Costs
If overtime from existing staff costs less than hiring additional employees with full benefits (health insurance, 401k, PTO), the math favors overtime.
Example: A distribution center calculates that 15 employees each working 5 hours of weekly overtime ($175,500 annually) costs less than hiring 2 full-time employees with benefits ($92,000 in wages + $28,000 in benefits = $120,000, but you’d need 2 to cover the hours = $240,000).
When Overtime Hurts Your Business
Here’s when overtime is destroying value:
1. Chronic, Predictable Overtime
If the same people work every single week overtime for months, you’re understaffed. Period.
Red flag: Any employee consistently working 45+ hours/week for 8+ consecutive weeks.
2. Emergency-Driven Overtime
Constant “emergency” overtime callouts mean your scheduling process is broken, or your baseline staffing is wrong.
Red flag: More than 15% of overtime hours are unscheduled emergency fill-ins.
3. Overtime Masking Inefficiency
Using extra hours to compensate for poor processes, outdated equipment, or inadequate training is expensive denial.
Red flag: Productivity per hour (units/hour) is declining even as total hours increase.
4. Burnout-Level Overtime
When employees work 55+ hour weeks regularly, you’re accelerating turnover and risking safety incidents.
Red flag: Turnover rate increases within high-overtime departments.
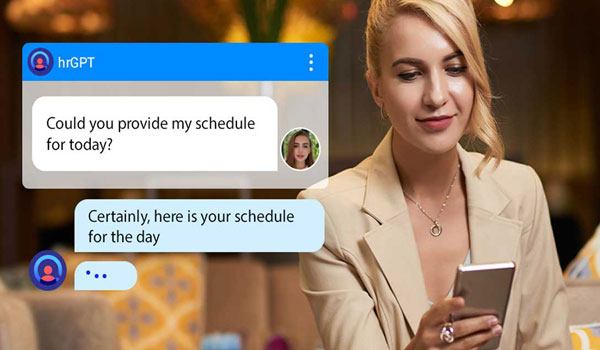
Identifying Your Overtime Root Causes
Before you can manage overtime, you need to understand why it’s happening. Run this diagnostic:
Data Analysis (Use UKG Reports):
- Overtime Distribution Report
- Who’s working overtime? (Top 20% of employees usually account for 60% of OT)
- Which departments/locations have the highest OT percentage?
- What days/shifts see the most overtime?
- Planned vs. Unplanned Overtime
- How much OT is scheduled in advance vs. emergency fill-ins?
- What’s triggering unplanned overtime? (call-outs, no-shows, demand spikes)
- Overtime by Reason Code
- Coverage for absences
- Increased workload/demand
- Special projects
- Training
- Voluntary vs. mandatory
- Productivity Correlation
- Are you getting proportional output from overtime hours?
- Compare productivity metrics during regular hours vs. OT hours
The Five Root Causes (And How to Spot Them):
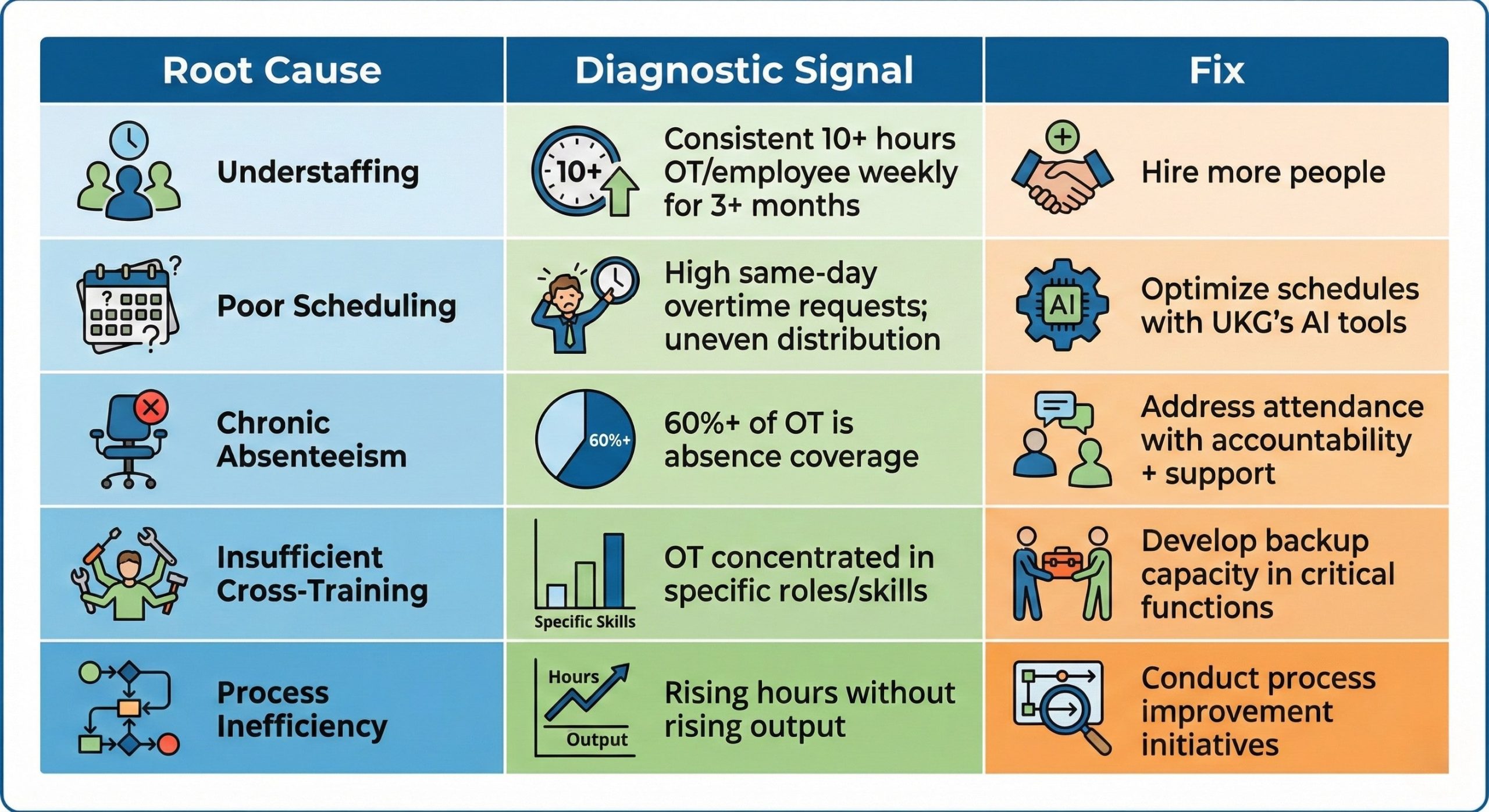
UKG Overtime Tracking and Alerts: Your Control Center
UKG provides powerful overtime management tools—if you configure them correctly.
Essential UKG Overtime Configurations:
- Real-Time Overtime Tracking Dashboard Set up manager dashboards showing:
- Employees approaching 40 hours (with hours remaining)
- Current week OT hours by employee/department
- Projected weekly OT based on scheduled shifts
- Budget vs. actual OT spend
- Automated Manager Alerts Configure UKG to notify managers when:
- Employee hits 37-38 hours (warning threshold)
- Employee scheduled to exceed 40 hours
- Department OT budget reaches 80% of weekly allocation
- Unscheduled overtime punches occur
- Pre-Shift Overtime Warnings Enable the setting that prevents managers from scheduling shifts that would create overtime without explicit approval.
- Daily Overtime Summary Reports Automated emails each morning showing:
- Yesterday’s OT hours by department
- Running weekly total
- Employees nearing overtime thresholds today
UKG Reporting for Overtime Analysis:
Run these reports monthly:
- Overtime Detail Report: Every OT hour, by employee, with reason codes
- Overtime Trend Report: Month-over-month and year-over-year comparisons
- Department Overtime Ranking: Which departments are over/under budget
- Employee Overtime Distribution: Identify OT hogs vs. equitable distribution
hrPad’s Real-Time Overtime Warnings: Prevention at the Point of Clock-In

Here’s where CloudApper hrPad transforms overtime management from reactive to proactive.
Employee-Facing Overtime Awareness:
When an employee clocks in on an hrPad kiosk, the system automatically displays their overtime status:
Scenario 1: Approaching Overtime
“You’ve worked 37.5 hours this week. You have 2.5 regular hours remaining before overtime.”
Scenario 2: Overtime Shift
“This shift will include 3 hours of overtime. Your manager has approved this overtime.”
Scenario 3: Unapproved Overtime Risk
“Clocking in now will create unapproved overtime. Please see your supervisor before starting your shift.”
Manager-Facing Real-Time Alerts:
hrPad sends instant SMS notifications to managers when:
- An employee clocks in for an unapproved overtime shift
- An employee’s hours approach the 40-hour threshold
- Overtime hours exceed weekly budgeted amounts
- An employee attempts to clock in early (creating unexpected OT)
The Photo Attestation Game-Changer:
When overtime occurs, hrPad can require:
- Photo capture at clock-in (confirming identity, preventing buddy punching)
- Manager approval code entry on the kiosk
- Reason code selection by the employee (“Covering absence,” “High demand,” “Special project”)
This creates a documented audit trail for every overtime hour—essential for FLSA compliance and cost control.
Geofencing Prevents Off-Site OT Fraud:
hrPad’s geofencing ensures employees can only clock in from approved locations, preventing:
- Early clock-ins from home before arriving at work
- Unauthorized remote work claiming overtime
- Time theft schemes
Manager Approval Workflows: Who Approves What, When
Clear approval workflows prevent overtime creep. Here’s a proven three-tier system:
Tier 1: Scheduled Overtime (Approved in Advance)
Threshold: Any overtime scheduled more than 24 hours in advance
Approval Process:
- Manager identifies need and creates an overtime-generating schedule
- UKG flags the schedule for overtime approval
- Department head reviews and approves via UKG or hrPad
- Employee can see approved overtime shift on their schedule
- No additional approval needed at clock-in
Use for: Planned coverage, known demand spikes, scheduled projects
Tier 2: Same-Day Overtime (Manager Discretion)
Threshold: Overtime needed within 24 hours (emergencies, call-outs)
Approval Process:
- Manager identifies need due to absence or demand
- Manager approves in UKG or provides approval code
- Employee clocks in on hrPad with manager’s approval code
- Overtime is automatically documented as “emergency coverage”
Use for: Unexpected absences, sudden demand increases
Tier 3: After-the-Fact Overtime (Requires Explanation)

Threshold: Employee works overtime without pre-approval
Approval Process:
- hrPad flags unauthorized overtime and alerts manager via SMS
- Manager must review and either:
- Approve with reason code (system accepts the OT)
- Deny and investigate (potential policy violation)
- If denied, triggers disciplinary process and employee counseling
- Pattern of unauthorized OT = progressive discipline
Use for: Catching policy violations, identifying training gaps
Budget Escalation Rules:
Configure automatic escalation in UKG:
- 10% over weekly OT budget → Department head notification
- 20% over → Director approval required for additional OT
- 30% over → VP/CFO must approve (triggers cost control review)
Alternative Strategies to Overtime: Building Flexible Capacity
The best overtime management strategy is having alternatives. Here’s your toolkit:
Strategy 1: Part-Time Workforce Expansion
The Math:
- 2 part-time employees at 25 hours/week each = 50 hours of coverage
- Cost: 50 hours × $18/hour = $900/week
- Alternative: 1 full-time employee + 10 hours OT = (40 × $18) + (10 × $27) = $990/week
- Savings: $90/week = $4,680/year per position
Implementation:
- Hire specifically for peak hours/days
- Offer limited benefits (may still be cost-effective)
- Create “float pool” of part-timers available for any department
- Use hrPad’s shift bidding to let part-timers claim available hours
Best for: Predictable weekly demand fluctuations, weekend coverage, meal period relief
Strategy 2: Shift Optimization
Audit your current schedules for:
- Unnecessary overlap periods (two shifts with 1-hour overlap = wasted hours)
- Peak vs. off-peak misalignment (staffing evenly when demand isn’t even)
- Shift length inefficiencies (8.5-hour shifts that regularly become 9.5 with OT)
UKG’s AI scheduling can:
- Analyze historical demand patterns
- Recommend optimal shift start/end times
- Suggest split shifts for peak periods
- Identify gaps and overlaps
Example: A restaurant shifted from 10am-6pm and 5pm-11pm shifts (1-hour overlap) to 10am-5pm and 6pm-12am (1-hour gap covered by manager). Eliminated 7 overlap hours/day = 49 hours/week = $1,323/week savings.
Strategy 3: Process Improvement
Ask: “Why does this task take so long?”
Common time wasters that generate overtime:
- Waiting for equipment/materials (poor inventory management)
- Rework due to quality issues (inadequate training/tools)
- Manual processes that should be automated
- Unclear procedures causing confusion and delays
- Excessive meetings or paperwork
Process improvement ROI: A warehouse reducing order-picking time by 12% through better organization eliminated 60 hours of weekly overtime (5 employees × 12 hours each) = $94,000 annual savings.
Strategy 4: Strategic Cross-Training
The Overtime-Cross-Training Connection:
Overtime often spikes in specialized roles because “only Sarah can do this.” When Sarah’s out sick, you’re forced into expensive emergency overtime with the next-available trained person.
Cross-Training Investment:
- Identify your top 5 overtime-generating roles
- Train 2-3 backup employees in each role
- Track certifications in UKG
- Use hrPad to display employee certifications for scheduling
ROI Example: Training 3 backup forklift operators (30 hours of training time × $18/hour = $540 per person = $1,620 total) eliminated 80 hours of annual emergency overtime callouts at premium rates = $3,600 savings = 122% first-year ROI.
Mandatory vs. Voluntary Overtime Policies: Finding the Balance
Your overtime policy needs to address a fundamental question: Can you require employees to work overtime?
Voluntary Overtime Model
How it works:
- All overtime is offered, never mandated
- Employees opt in to OT opportunities
- First-come, first-served or seniority-based allocation
- No penalties for declining overtime
Pros: ✅ Higher employee satisfaction and morale ✅ Lower turnover risk ✅ Employees work OT because they want to (better attitude) ✅ Attracts workers who value work-life balance
Cons: ❌ Coverage gaps when no one volunteers ❌ May need to offer premiums beyond 1.5x to incentivize ❌ Can’t guarantee coverage for critical needs
Best for: Retail, hospitality, non-critical operations, companies competing for talent
Mandatory Overtime Model
How it works:
- Employees can be required to work beyond scheduled hours
- Refusal to work mandatory OT = policy violation/discipline
- Usually includes advance notice requirements (24-48 hours when possible)
- Rotation systems to distribute burden fairly
Pros: ✅ Guaranteed coverage for business needs ✅ Predictable staffing for demand spikes ✅ Works in 24/7 critical operations
Cons: ❌ #2 cause of frontline employee turnover ❌ Can trigger burnout and resentment ❌ Some states limit mandatory OT (healthcare workers) ❌ May violate union contracts
Best for: Manufacturing, healthcare, distribution, public safety, utilities
Hybrid Model (Recommended for Most Organizations)
How it works:
- All OT is voluntary by default
- Company reserves the right to mandate OT in specific circumstances:
- Emergencies (natural disasters, system failures)
- Critical business needs (major client shipments, product launches)
- When voluntary OT fails to fill needs
- Mandatory OT limited to X hours per week/month (e.g., 10 hours/week max)
- Advance notice required except for true emergencies
- The rotation system ensures fair distribution
Policy Language Example:
“Overtime is voluntary whenever possible. The company reserves the right to require mandatory overtime when business needs cannot be met through voluntary participation. Mandatory overtime will be distributed fairly using a rotating system and will be limited to 10 hours per week per employee except in emergency situations. Employees will receive at least 48 hours advance notice of mandatory overtime except in true emergencies.”
Using hrPad for Equitable OT Distribution
Configure hrPad to:
- Display OT leaderboard (who’s worked most/least OT this month)
- Show each employee their OT total vs. the department average
- Enable “OT bid” feature where employees claim available OT shifts
- Track mandatory OT rotations to ensure fairness
Transparency kills favouritism complaints.
Legal Requirements by State: Staying Compliant
Overtime law is more complex than “40 hours = time-and-a-half.” Here’s what you need to know:
Federal Law (FLSA):
- Non-exempt employees: OT after 40 hours in a workweek
- Rate: 1.5x regular rate of pay
- Workweek defined by employer (doesn’t have to be Sun-Sat)
- No daily OT requirement (federal)
- No maximum OT hours (adults)
State-Specific Rules to Watch:
California (Most Restrictive):
- OT after 8 hours in a day OR 40 hours in a week
- Double-time after 12 hours in a day
- 7th consecutive workday = OT (first 8 hours), double-time (hours 8+)
- No meal/rest period = 1 hour of pay penalty
Alaska:
- OT after 8 hours/day OR 40 hours/week
Colorado:
- OT after 12 hours/day OR 40 hours/week
- Daily OT applies to specific industries
Nevada:
- OT after 8 hours/day if earning less than 1.5x minimum wage
- Otherwise, 40 hours/week standard
Healthcare Workers (Multiple States):
- Some states prohibit mandatory OT for nurses
- Advance notice requirements
- Consecutive shift limitations
UKG Configuration for State Compliance:
Ensure your UKG system is configured for:
- Correct state OT rules (daily vs. weekly)
- 7th-day premium calculations
- Meal/rest period tracking with auto-penalties
- Minor hour restrictions (if applicable)
hrPad enhances compliance by:
- Automatically calculating OT based on state rules
- Warning employees when approaching daily OT thresholds
- Documenting meal breaks with clock-in/out attestation
- Providing audit trail for FLSA/state labor investigations
The Overtime Management Dashboard: Your Weekly Ritual
Create a 15-minute weekly overtime review ritual using UKG data displayed on your hrPad manager portal:
Every Monday Morning:
- Review last week’s OT: Total hours, cost, vs. budget
- Identify top OT earners: Are the same 5 people always on the list?
- Analyze reasons: Demand spike, call-outs, inefficiency, understaffing?
- Check distribution: Is OT fairly distributed or concentrated?
- Preview this week: Any scheduled shifts creating predicted OT?
- Action items: What needs to change this week?
Dashboard Metrics to Track:
- OT Hours as % of Total Hours: Industry benchmark is 4-8%; over 12% is a red flag
- OT Cost as % of Total Payroll: Should be 6-12%; over 15% indicates problems
- Average OT Hours per Employee: Should be under 3-4 hours/week for most businesses
- OT Distribution (Gini Coefficient): Measures fairness; closer to 0 = evenly distributed
- Planned vs. Unplanned OT Ratio: Should be 70/30 or better
Putting It All Together: Your 90-Day Overtime Optimization Plan
Days 1-30: Assess and Configure
- Run comprehensive OT reports in UKG (last 6 months)
- Identify root causes using diagnostic framework
- Configure hrPad overtime warnings and alerts
- Set up manager approval workflows
- Establish OT budget by department
Days 31-60: Implement Alternatives
- Launch cross-training program for top OT roles
- Hire part-time workforce where math supports it
- Optimize schedules using UKG’s AI recommendations
- Roll out shift bidding through hrPad
- Communicate new OT policies to employees
Days 61-90: Monitor and Adjust
- Track OT reduction progress weekly
- Gather employee feedback on new policies
- Adjust staffing levels based on data
- Refine approval workflows based on patterns
- Calculate ROI and savings
Expected Results:
- 30-40% reduction in unplanned overtime
- 15-25% reduction in total OT hours
- 20-30% improvement in OT distribution fairness
- $50,000-$200,000 annual savings (depending on organization size)
The Bottom Line
Overtime isn’t inherently good or bad—it’s a tool. Like any tool, its value depends on how intentionally you use it.
Uncontrolled overtime is a symptom of deeper problems: poor planning, inadequate staffing, broken processes, or weak management. It inflates costs, burns out employees, and masks inefficiencies you should be fixing.
Strategic overtime is a legitimate business tool for handling variability, retaining employees who value extra income, and avoiding the costs of unnecessary permanent hiring.
The difference comes down to three things:
- Visibility: Real-time data through UKG and hrPad that shows you exactly where OT is happening and why
- Control: Approval workflows and alerts that prevent OT from spiraling out of control
- Alternatives: A toolkit of strategies that give you options beyond defaulting to overtime
When you combine UKG’s powerful workforce analytics with hrPad’s real-time employee engagement and manager alerts, you transform overtime from a necessary evil into a strategic advantage.
Your employees get transparency about their hours and earning opportunities. Your managers get the tools to control costs without constant firefighting. Your business gets predictable labor expenses and a more sustainable workforce model.
Start this week: Run your overtime analysis report, configure your first hrPad alert, and implement one alternative strategy.
Three months from now, you’ll look at your OT line item and smile instead of cringe.